- Fax: +86-519-85808128
- Url:www.aozhongw.com
- E-mail:YJX@aozhongw.com
- Add: NO.31,Xinke West Road,Luoyang Town,Wujin District,Changzhou City,Jiangsu Province,China

1. Welding of thick plate and thin plate
1. When welding steel workpieces with GMAW and FCAW, if the plate thickness of the workpieces exceeds the maximum welding current that the welder can achieve, what will be done?
The solution is to preheat the metal before welding. The welding area of the workpiece is preheated with propane, gas or acetylene welding torch specified in the standard, and the preheating temperature is 150 ~ 260℃, and then welding is performed. The purpose of preheating the metal in the welding area is to prevent the weld area from cooling too fast, so that the weld does not crack or fail to fuse.
2. If a thin metal cover is welded to a thick steel pipe by MIG welding or flux-cored wire gas shielded welding, if the welding current is not properly adjusted during welding, two situations may occur: first, the welding current is reduced to prevent the thin metal from burning through, and the thin metal cover cannot be welded to the thick steel pipe at this time; Second, too much welding current will burn through the thin metal cover. What should be done in this case?
There are two main solutions: (1) Adjust the welding current to avoid burning through the thin metal cover, and use the welding torch to preheat the thick steel pipe, and then use the sheet welding process to weld the two-metal structure. ② Adjust the welding current to be suitable for the welding of thick steel pipes. When welding is performed, the residence time of the welding arc on the thick steel pipe is maintained to be 90%, and the residence time on the thin metal cover is reduced. Only when you are proficient in this technology can you get a good welded joint.
3. When welding a thin-walled round tube or rectangular thin-walled tube to a thick plate, the welding rod is easy to burn through the thin-walled tube part. In addition to the above two solutions, are there other solutions?
Yes, a cooling rod is mainly used in the welding process. If a solid round rod is inserted into a thin-walled round pipe, or a solid rectangular rod is inserted into a rectangular pipe fitting, the solid rod will take away the heat of the thin-walled workpiece and prevent burning through. In general, solid round or rectangular rods are tightly installed in most supplied hollow pipe or rectangular pipe materials. When welding, care should be taken to keep the weld away from the end of the pipe, the end of the pipe is the most prone to burn through the weak area. The use of a built-in cooling rod to avoid burning through is shown in Figure 1.
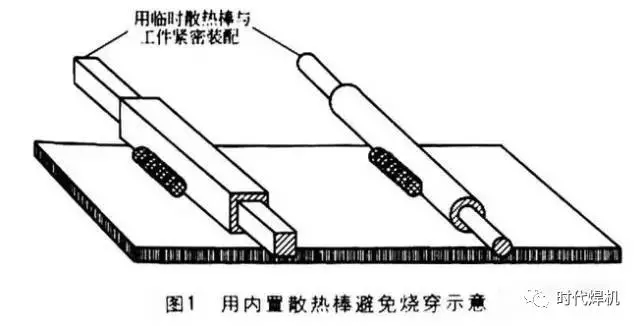
4. When galvanized or chromium-containing material must be welded with another part, how should it be operated?
**** The process is to file or sand the area around the weld before welding, as galvanized or chromium-containing metal sheets not only contaminate and weaken the weld, but also release toxic gases during welding.
2. Welding of container and frame structure
1. If a float or the end of a hollow structure is sealed by a welding process (e.g. brazing), what should be done to prevent hot air from entering the container and causing it to burst during the final sealing of the weld?
A pressure relief hole with a diameter of 1.5mm is drilled into the buoy first to facilitate the circulation of hot air near the weld to the outside air, then the sealing welding is performed, and finally the sealing pressure relief hole is welded. The diagram of a sealed-welded buoy or closed container is shown in Figure 2. When welding the structure of the gas storage vessel, pressure relief holes can also be used. It should be noted that welding in a closed container is very dangerous, and should ensure that the inside of the container or pipe is clean before welding, and avoid the presence of flammable and explosive items or gases.
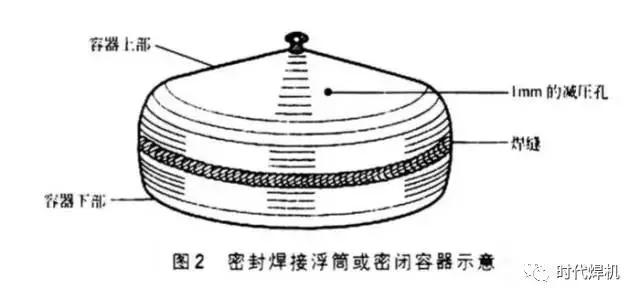
2. When it is necessary to use MIG welding, flux-cored wire gas welding or argon tungsten arc welding to weld the screen grid, wire mesh or extension metal to the steel structure frame, the wire mesh is prone to burn through and the weld seam is not fused, how to deal with it?
(1) Place non-metallic washers on wire mesh or extended metal and clamp the washers, wire mesh and frame together. Chromium or galvanized washers are not allowed. The washers should be uncoated, as shown in Figure 3(a).
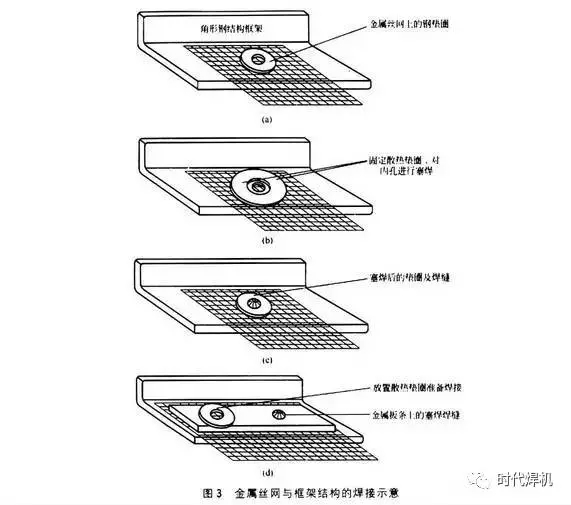
② Place a larger washer above the washer in the welded position as a heat sink. The upper washer should have a larger hole than the lower washer to avoid the upper washer also being welded together. Plug welding is then performed through the two holes of the washer so that the weld is in the lower washer part. The operator can take some other methods to obtain sufficient heat and weld, taking care to prevent the surrounding screen or wire mesh from burning through, see Figure 3(b) and (c).
③ Another method is to use a metal strip with holes, align the holes with the parts that need to be welded, and place the cooling washer, and then plug welding, see Figure 3(d).
Copyright: Changzhou Aozhong Special Welding Wire Co., LTD.